
Naming your gateway not the same as naming a gateway subnet. On the Basics tab, fill in the values for your virtual network gateway. This opens the Create virtual network gateway page. On the Virtual network gateway page, select Create. Locate Virtual network gateway in the search return and select the entry.
In the Search the Marketplace field, type ‘Virtual Network Gateway’. Microsoft recommends that you create a gateway subnet that uses a /27 or /28. Creating a gateway can often take 45 minutes or more, depending on the selected gateway SKU. In this step, you create the virtual network gateway for your VNet. Select Review + create to validate the virtual network settings.Īfter the settings have been validated, select Create.

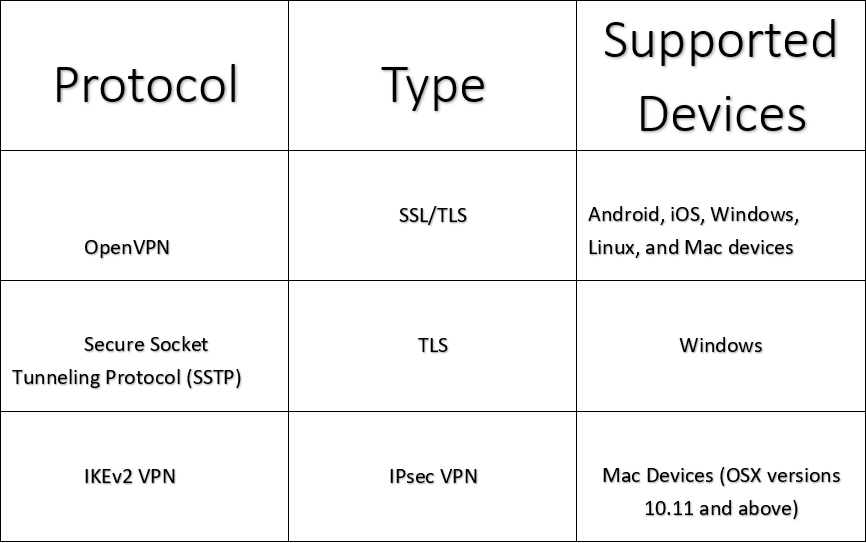
The values shown in the examples below are for demonstration purposes. On the IP Addresses tab, configure the values. Public IP address name: NestedVnetGWpip.Virtual network gateway name: NestedVnetGW.Subscription: If you have more than one subscription, verify that you are using the correct one.You can have more than one address space for your VNet. You can use the following values to create a test environment, or refer to these values to better understand the examples in this article:įor this example, we use only one address space. On the Basics tab, configure Project details and Instance details VNet settings. Once you select Create, the Create virtual network page opens. On the Virtual Network page, select Create. Select Virtual Network from the Marketplace results In Search resources, service, and docs (G+/), type virtual network P2S creates the VPN connection over either SSTP (Secure Socket Tunneling Protocol), or IKEv2. Point-to-Site connections do not require a VPN device or a public-facing IP address. You can also use P2S instead of a Site-to-Site VPN when you have only a few clients that need to connect to Azure. Point-to-Site VPN connections are useful when you want to connect to Azure from a remote location, such as when you are telecommuting from home or a conference.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
